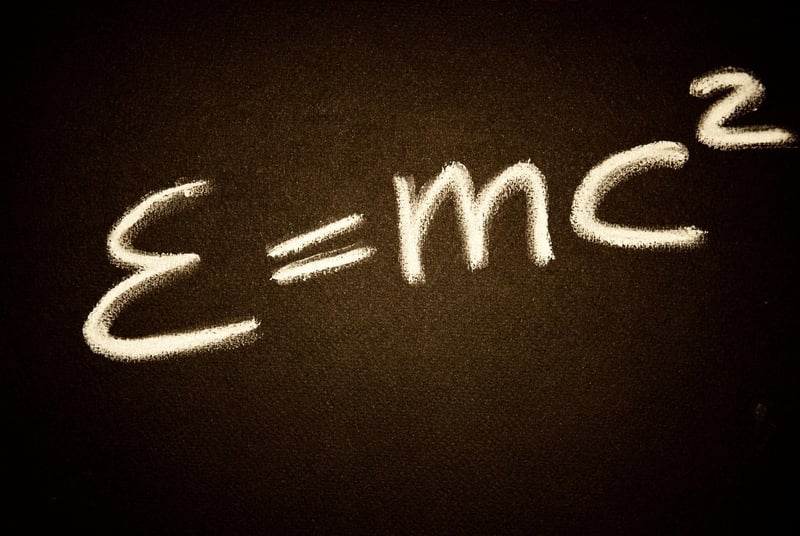Relativity Effects
Understanding Time in Space and Relativity Effects
Time, a fundamental aspect of our existence, behaves differently in the vast expanse of space due to the effects of relativity. Let's delve into the intriguing world of time dilation and how it impacts our perception of time.
Time Dilation in Space
According to Einstein's theory of relativity, time is not a constant but is relative and can be influenced by various factors, such as gravity and velocity. Time dilation is a phenomenon where time moves at different rates depending on the speed of an object and the strength of the gravitational field it is in.
Effects of Gravity
As gravity increases, time slows down. This means that time passes more slowly in stronger gravitational fields. For instance, a clock closer to a massive object like a planet will tick slower than a clock farther away in space.
Effects of Speed
As an object moves faster, time also slows down relative to a stationary observer. This concept, known as time dilation, has been experimentally verified through various experiments, including the famous Hafele-Keating experiment involving atomic clocks on airplanes.
Practical Applications
The effects of time dilation are not just theoretical but have practical implications. Technologies such as GPS satellites need to account for the time difference caused by both their speed and the weaker gravitational field in orbit compared to the Earth's surface.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of time in space and the effects of relativity opens up a whole new perspective on the nature of our universe. Time, once thought of as a constant, is now seen as a dynamic and relative concept that is intertwined with the fabric of spacetime.

Explore more about the wonders of space and time to uncover the mysteries that lie beyond our everyday perception.